The human experience is shaped by five basic senses, one of which is touch. As we move further into the realms of virtual environments and augmented reality, the importance of touch increases. A simple touch can enhance the sense of reality and bridge the gap between the physical and the digital.
This blog post seeks to explain the basics of EMS and TENS as a type of haptic feedback technology. From sports training to mental health rehabilitation and safety training for the manufacturing industry, let’s explore the possibilities of these technologies and see how they are transforming the way we interact with the digital and real world.
How does EMS and TENS work?
Before we dive into what EMS and TENS are, let’s explore the basics of haptics. Haptic technology allows you to receive tactile information through sensations by applying force, vibration or touch. Haptics simulates interactions with the virtual system or whole objects by creating sensations as if they were real. There are several types of haptic technologies, but here we will look at Electromyostimulation and Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation.
Electromyostimulation (EMS), also known as Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES), uses controlled electrical impulses to stimulate muscles, causing involuntary contractions that contribute to a more immersive virtual world experience. EMS is intended to strengthen muscles and speed up muscle recovery. It is typically used for muscle recovery. NMES works simply by sending electrical impulses that artificially activate muscles, causing them to contract and relax as if they were working.
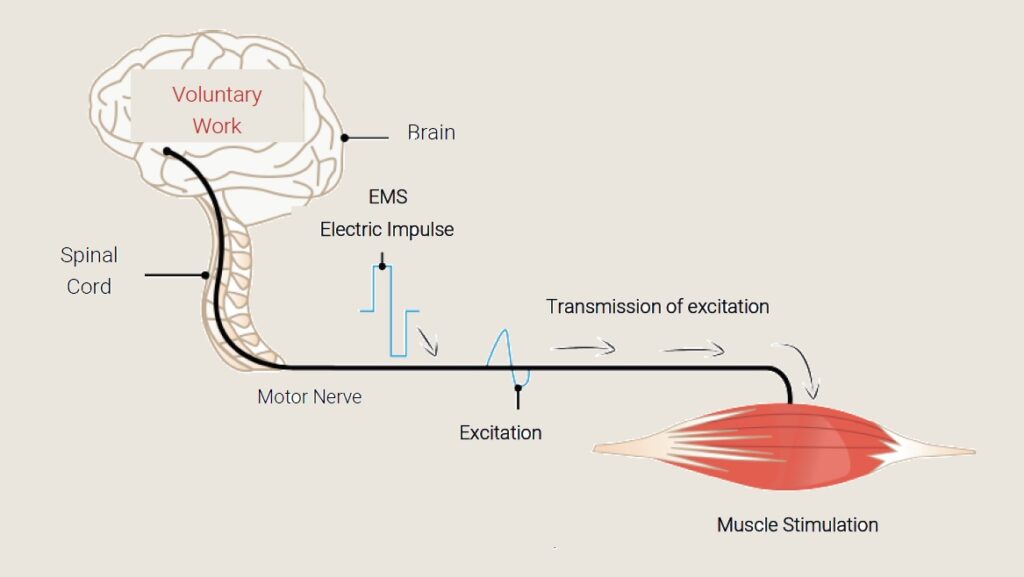
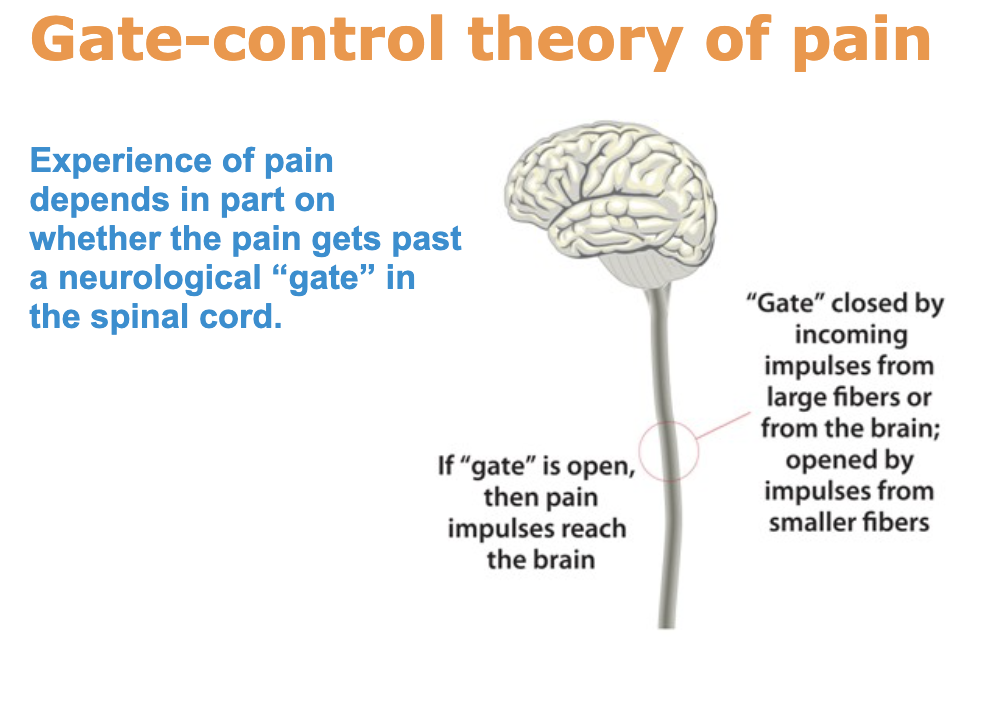
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), in contrast, sends low-voltage electrical currents across the skin to stimulate nerves, providing a unique form of tactile feedback that bridges reality and simulation. This technique is most commonly used for temporary relief of sore and aching muscles or to relieve chronic pain. TENS uses natural pain relief mechanisms such as the pain gate theory to relieve chronic pain. When TENS is applied, it stimulates sensory nerve fibres, overriding the nerves that normally transmit the pain signal to the brain. This closes the pain gate, reducing the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
Possible Applications
EMS and TENS are best known for their use in rehabilitation and sports. However, they are not limited to these applications. Other areas that could benefit from the integration of EMS and TENS technologies include VR gaming and mental health therapy. As a wearable suit, TESLASUIT can make it even easier to apply EMS and TENS in different areas. When we talk about a wearable haptic suit, the range of applications is limited only by imagination.
Enterprise Safety Solutions
By integrating haptic technology, EMS and TENS can be used to simulate hazardous scenarios, allowing workers to train in a safe environment. Some studies have shown that EMS can simulate the weight of heavy machinery, while TENS can mimic the sensation of electric shock. This hands-on, risk-free approach can improve the safety awareness of workers, thereby reducing the number of accidents and injuries at the workplace.
TESLASUIT’s haptic feedback was used for creating an effective and cost-saving virtual reality training course for power engineers aimed at improving the learning experience by increasing immersion in a production process while avoiding occupational risks.
Sports Training
Imagine how athletes can train in a virtual arena. This is where the TESLASUIT’s fusion of haptics – EMS and TENS – comes into play. With EMS, every muscle contraction provides real-time feedback on effort. This experience could drive athletes to peak performance. At the same time, TENS provides relief, helping to recover after training and relieving muscle soreness.
In 2019, Vodafone held a world-first demonstration of the power of 5G to transmit touch using the TESLASUIT’s haptic technology. Two players from Wasps rugby team were able to run a training session despite being more than 100 miles apart. The impact of a rugby tackle made by Will Rowlands at the Ricoh stadium in Coventry was transferred via 5G to teammate Juan de Jongh on stage in London. De Jongh, in a full-body haptic suit, was able to feel the force of the tackle in realtime.
Rehabilitation
In the hands of skilled therapists, haptic technologies are paving the way for targeted muscle re-education and nerve stimulation. EMS facilitates muscle rebuilding, helping to regain strength and movement after injury. Meanwhile, TENS provides an avenue for pain management, offering comfort and relief to those on the journey to recovery. Together, EMS and TENS become an invaluable tool in the hands of rehabilitation specialists.
VR Gaming
Speaking of VR, EMS and TENS can transform the VR experience, creating immersive adventures that resonate beyond the screen. The thrill of VR gaming is enhanced by EMS, which makes every punch, every leap a tangible experience. At the same time, TENS adds depth to the encounter, providing nuanced feedback that blurs the lines between the real and the virtual. Together, EMS and TENS, along with TESLASUIT, become a game changer.
Feel the Drive became the world-first multi-sensory driving experience delivering an unprecedented level of immersion. TESLASUIT’s haptic feedback system replicated the acceleration, g-force, gear change and braking of Lewis Hamilton’s victorious 2018 pole lap. Every vibration and force is translated to the body by the haptic sensors, which are synched to the data collected from his car, giving unparalleled insight into the technique of one of the most successful F1 drivers of all time.
Mental Health Therapy
EMS and TENS also have the potential to be used as a therapeutic tool in mental health care. Researchers from Siegin University have proven that the TESLASUIT’s haptic feedback technology can be used to create immersive experiences that help patients confront and manage anxiety.

In addition, the research study “A calming hug: Design and validation of a tactile aid to ease anxiety” has shown that haptic technology can even be used to create an interface similar to a person’s hug that reduces anxiety. Such studies are evidence of how EMS and TENS can be helpful in the treatment of mental health conditions.
Conclusion
As we learn more about the range of EMS and TENS technologies, it becomes clear that their influence goes far beyond the applications covered above. With the help of EMS and TENS, we can rethink the interaction between the virtual and real worlds, especially in the areas of safety training, VR gaming, sports training, rehabilitation and mental health therapy.
The future holds even more promise for both EMS and TENS technologies, as innovation continues to push the boundaries of what is possible. With the integration of motion capture, biometrics and haptic technology, TESLASUIT is at the forefront of these developments, opening the door to exciting use cases across a wide range of industries.
