There is a huge variety of wearable devices. Nevertheless, there is no generally accepted classification of wearables. So in this article, we divided them into different types to create as comprehensive classification as possible.
Let’s start with wearables definition. Wearables are electronic devices with embedded sensors that can receive data about a human who wears them or/and about the surrounding environment. These devices work wirelessly or by dint of other devices like smartphone or tablet. Wearables send information to the processing unit, which can be inbuilt or located on an external server, and processed information transfers to the user.
In general terms wearable smart devices are divided by IEC (The International Electrotechnical Committee) into the following types:
– near-body electronics;
– on-body electronics;
– in-body electronics;
– electronic textiles.
Also, research companies often divide wearables into submarkets.
This is an example of Berkeley typology:
– smart watches;
– smart glasses;
– smart clothing;
– fitness trackers;
– body sensors;
– wearable cameras;
– other.
Gartner presents a little bit different classification of wearables:
– smart watches;
– head-mounted displays;
– body worn cameras;
– bluetooth headsets;
– wristbands;
– smart garments;
– chest straps;
– sports watches;
– other fitness monitors.
Here is our own classification of wearable devices. Please, note that some of the wearables are used with the word “smart” and some are not. It depends on the usability of these names. Besides, it is worth remembering that there is no distinct terminology of garments.
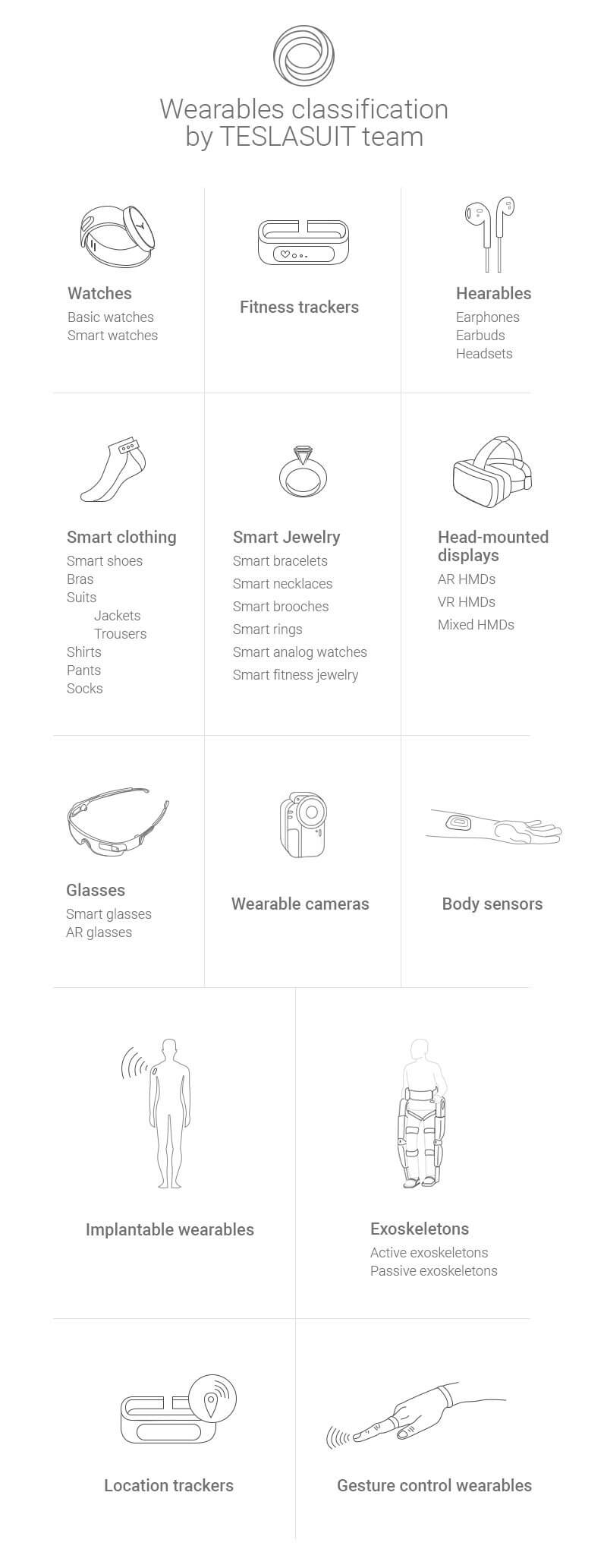 Watches
Watches
Basic watches differ from smart watches by inability to support third-party applications.
Watches market share became so large in wearables that independent sub-segments have begun to stand out. Such niches are kids’ watches, fashion watches, athletic watches, and luxury.
At this moment smartwatch is the most popular wearable product. According to IDC forecast, these garments will be even more common in the future as represent devices that cover multiple functions.
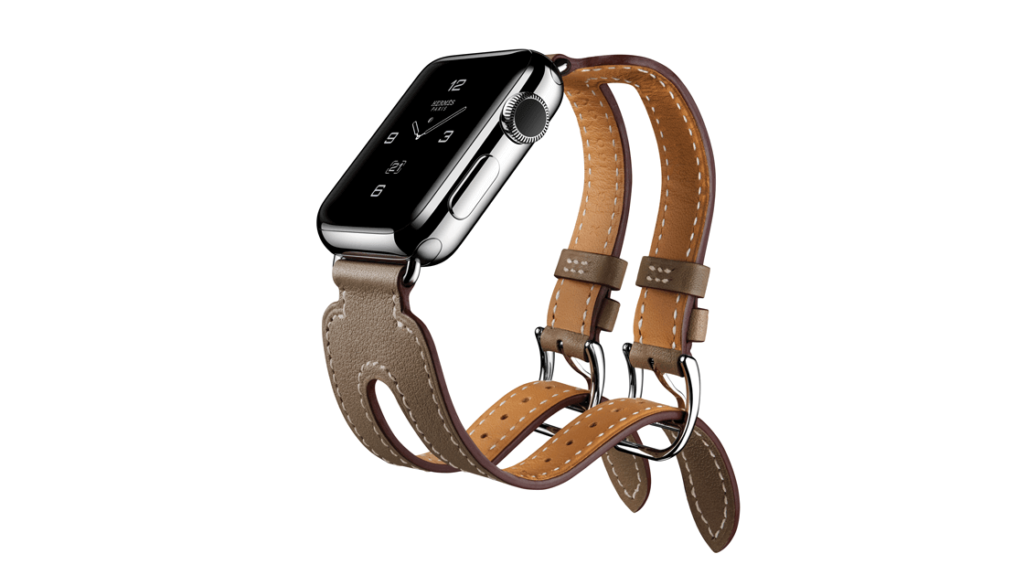

Apple watch Hermès. Image credit: Apple
Fitness trackers
In another way, such devices are called wristbands, as they are usually worn on the wrist. These appliances measure such metrics as distance walked or run, calorie consumption, heart rate and quality of sleep, etc.
As IDC predicts, wristbands will be in less demand in several years, because many of their functions are built into smartwatches.

Samsung Gear Fit2
Hearables
Hearables are similar to headphones. They allow voice input and give the result on request back to the user’s ear in audio format. In fact, it’s a micro computer in your ear.
Hearables may be divided into earphones, earbuds, and headsets. These concepts are confused very often, and sometimes are generalised as headsets.
Earphones (in-ear headphones or in-ears) are located in the ear canal. Generally, they have ear cushions and their size can vary. Earbuds are held outside the ear canal so you can hear ambient noise. Usually, they are of one size and, as a rule, are cheaper than earphones. Headsets are speakers or a speaker that are worn outside the ear/ears. They are equipped with a microphone.
Some hearables are more effective in determining body temperature or heart rate than wearables attached to the body, as hearables have a smaller margin of error.

Wireless smart earphones Bragi The Dash. Image credit: Bragi
Smart clothing
Smart clothing, or smart garments, are conductive fibers attached to or woven into the clothing material.
There are 3 generations of smart clothing according to Cientifica Ltd research. First generation garments are characterized by attaching to the apparel. Sensors are inserted into smart clothing of the second generation. And finally, third generation garments are sensors themselves.
There is a wide variety of smart garments such as shoes, bras, suits, shirts, pants, socks, etc. Perhaps, smart shoes are a more common wearable garment.
Smart shoes
Smart shoes gather stats such as distance, steps, stride rate and length, foot landing, time on the ground and so on. Most of these data can not be collected using trackers that are worn on a wrist.
This segment is in the initial stage of development but starts to emerge into a submarket.

Nike HyperAdapt 1.0. Image credit: Nike
Glasses
Smart glasses are wearable computer glasses that record information which the wearer sees and transfers data to сloud storage. AR glasses, in turn, add information to what the user sees.
AR glasses are supposed to become essential submarket, especially in USA and Asia Pacific region, particularly in Japan.
Announced in 2012, Google Glass was the first AR glasses, but they did not become mass product because of high cost and market immaturity. Mixed reality Hololens headed the trend in 2013. Then, in March 2016 full 90-degree Meta 2 was available for pre-order. A little bit later, in November 2016 Snapchat released fashionable Spectacles and promoted them greatly.

Spectacles by Snap Inc. Image credit: Spectacles
Smart jewelry
Smart jewelry appeared as a result of transferring smart watches’ functions into jewelry to attract more audience, especially women. Smart jewelry informs its owner about calls, emails or messages when the phone is far away. Also, such wearables track active minutes, calories burned, distance traveled and quality and duration of sleep. Some devices even can predict resistance to stress on the basis of data provided.
The range of smart jewelry is impressive: bracelets, necklaces, brooches, rings, analog watches and fitness jewelry are among them.

Bellabeat Leaf Urban Silver. Image credit: Bellabeat
Wearable cameras
Wearable cameras shoot video in a first-person perspective. As a rule, they are clipped on clothing, for example, shirt, hat or helmet. Wearable cameras record activities such as daily life, parties, and performances, sports, etc.
Some wearable cameras, such as GoPro can make a professional video up to 4K resolution. Most often, such cameras are used to shoot sports and adventure activities.

Narrative Clip 2. Image credit: Narrative
Body sensors
Body sensors may be implantable or may be located on the skin surface. They move together with the skin, сollect and send data to the connected computers or smartphones.
It is clear that body sensors are mostly applicable to medicine and healthcare. Body sensors may make electrocardiogram (ECG) and electroencephalogram (EEG) or check when a patient took his sensor-enabled pill. Also, body sensors track levels of physical activity and sleep patterns.

Microfluidic sensor for capture and analysis of sweat. Image credit: Northwestern University
The potential of body sensors lies in preventing pain and diseases.
There is some probability that body sensors market share will be larger than smart clothing’s one in the long run. It is due to a greater variety of devices, smaller size and a wider range of applications. But TESLASUIT team is inclined to believe that sensors and clothing will be as one. That is, when we talk about clothes, it will automatically mean smart garments.
Location trackers
Location trackers, or GPS-trackers, transmit the location of the wearer to the synchronized device.
GPS trackers for kids are becoming more popular. They specifically have a small size, while other standard devices, such as some of fitness trackers, are too bulky. Such devices allow to receive and make calls, play games, parents can even hear what is happening around their child. Parents also may set up reminders and activities. Having executed them, the child can receive bonuses.
Tinitell, GPS-tracker with mobile phone function. Image credit: Tinitell
It is difficult to say how this segment of devices will develop. On the one hand, the producers will strive for differentiating the devices and receive additional revenues. On the other hand, fitness trackers are universal and include almost the same functions and even more.
Head-mounted displays
Head-mounted displays, or helmets, are devices that allow a wearer to immerse himself or herself in the VR/AR/MR worlds. HMDs can create visual and acoustic effects of presence that is set by content creators.
HMD is designed to be worn on a head. The device, as a rule, consists of a display, lenses and an acoustic system. The name “helmet” is conventional, as modern models are much more like glasses than a helmet.
There are two main types of HMDs, monocular and binocular. Monocular head-mounted displays have display in front of one eye. As for binocular HMDs, they have a display together with a lense in front of each eye. The example of the monocular display is Google Glass.
Optical head-mounted displays (OHMDs) can be defined separately. They are devices with the ability to reflect the projected images and the wearer see the image as augmented reality.
Head-mounted displays market is still in its stage of formation. Consumer market of HMDs began to evolve energetically with the appearance of competing entertainment devices such as HTC Vive, Oculus Rift, Sony PlayStation VR, Samsung Gear VR, etc.
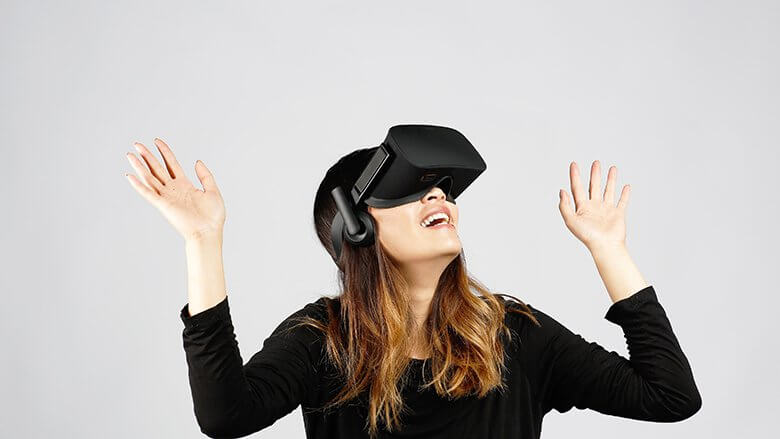

Oculus Rift. Image credit: Oculus
As a rule, HMDs are used in VR. Investors’ interest in VR is growing, and funding amounted $3 billion in 2016. SuperData, the leading provider of market research on digital games, estimates the VR market size at about $ 40 billion in 2020. Primarily, it will be related to the evolution of the gaming industry and the progress of mobile VR. So, head-mounted displays will continue to develop. For example, Microsoft VR headset may become a trendy wearable product with its competitive price, about $300.
Exoskeletons
The exoskeleton, or exosuit, is a machine that is power-driven by the combination of technologies such as electric motors, pneumatics, levers, hydraulics, and haptics. As a result, limbs can move with increased strength and endurance.
There are two main types of exoskeletons, active and passive.
Active exoskeletons have actuators that intensify user movements. Such devices are more common. They are applicable to medicine, military, civilian spheres. Paraplegic, paralyzed patients can walk with the help of skeletons. An example is Phoenix, a robotic exoskeleton. The suit returns movement to wearers’ knees and hips with the help of small motors attached to standard orthotics. Wearers can control the movement of each leg and walk by pushing the buttons.
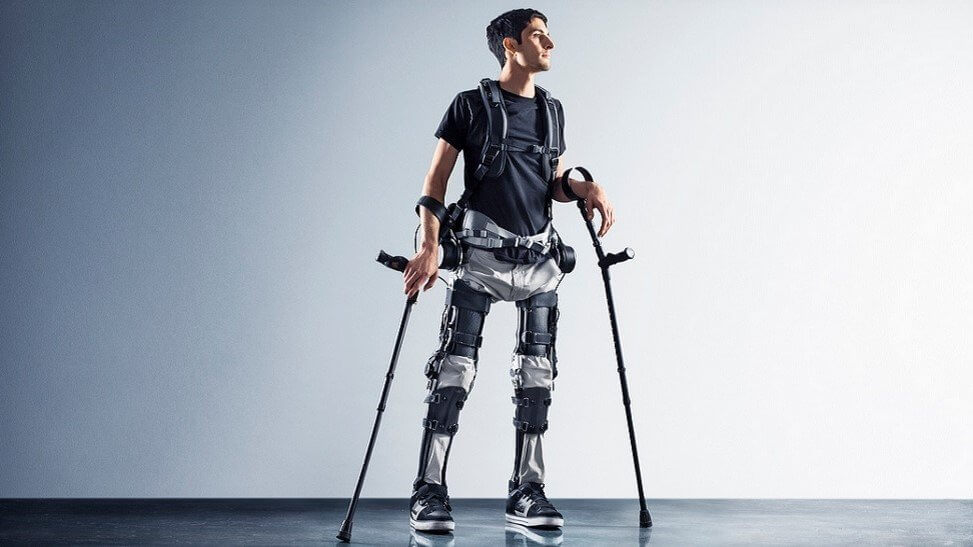

Phoenix exoskeleton by suitX. Image credit: suitX
Also, exosuits can ease manual labor for workers. Dangerous professions, such as firefighters, are becoming much safer if using exoskeletons.
Passive exoskeletons don’t have any actuators, batteries or electronics. These exoskeletons are used for military purposes, basically. For example, these machines can absorb shock and vibrations for military personnel or transfer some weight of a soldier’s backpack directly to the ground.
Gesture control wearables
Gesture control wearable is an appliance that distinguishes human body movements to transfer сertain information to the computer or other devices сarrying out hands-free control.
Such interface systems are usually called “natural user interface” meaning the absence of intermediate devices between the system and the user.
Most often such wearable devices are rings or wristbands. One of the most famous devices is Myo Armband. It makes managing phone or computers by arm movement possible, without touching it.

Myo Armband. Image credit: Myo
Implantable wearables
Implantable wearables are appliances inside the body that transfer data to a smartphone, computer or another device.
Medicine is the main driver sphere for implantable wearables. Smart monitoring and healing chips track blood-sugar level for diabetics. Cyber-pills are equipped with a microprocessor which contacts directly to the doctor’s smartphone application. In other words, implantable wearable devices simplify and speed up monitoring the patient’s state, and also accelerate the process of treatment due to real-time tracking.
Implanted RFID chips let track the location of people. Smart tattoos with the technology of Near Field Communication are able to interact with devices located at a small distance. A tattoo on the finger can unlock doors or enter codes by bringing the finger closer to the surface.
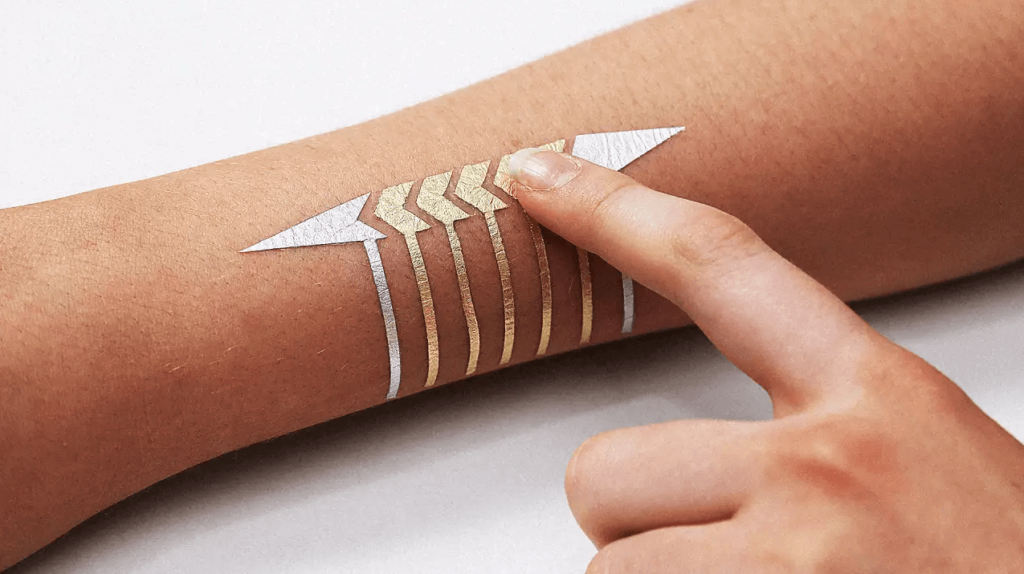

Duoskin electrical temporary tattoo by MIT Media Lab. Image credit: MIT Media Lab
Generalizing, there are numerous kinds of wearables, and universal classification doesn’t exist. Sometimes the smart garment is difficult to be attributed to one sort of wearables, as it can relate to several types at once. For example, once in a way head-mounted displays and AR glasses can be confused as they mean almost the same due to a simplistic minimalist design of HMDs.
Of course, as the market develops the classification of wearables will also change. Apparently, new species of smart garments will appear on the market.
If you want to ask any specific details, feel free to contact us or comment below.
Read our next articles concerning wearables market overview if you want to know more about the current state of the market and its forecasts.
